Meet The Blue Jay, A Bird That Sounds An Alarm Call When Hawks Or Other Dangers Are Near, And Smaller Birds Often Recognize It And Hide
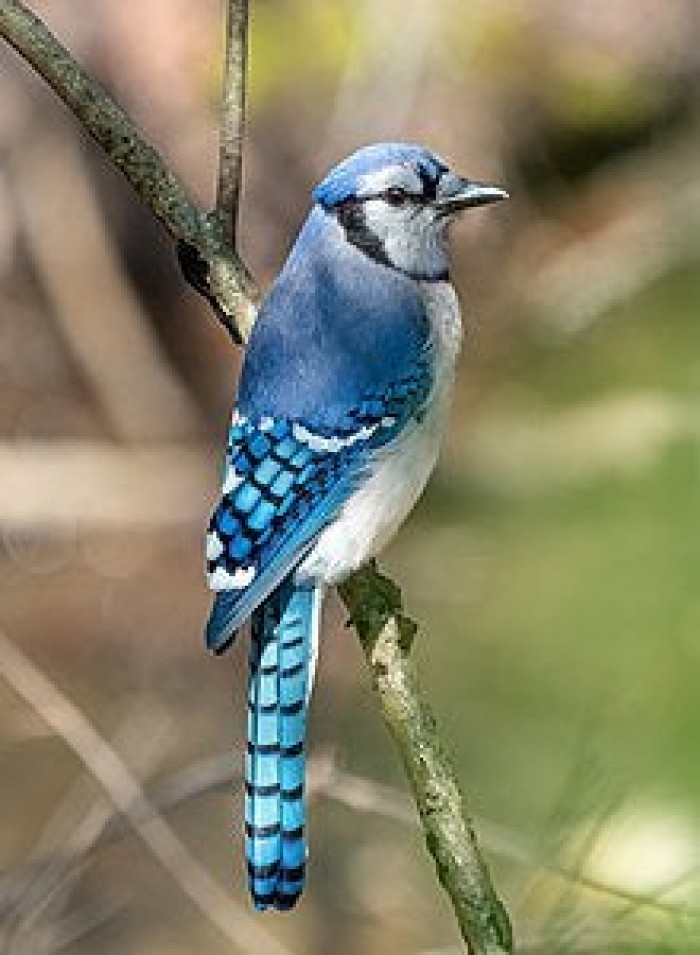
Eastern North America is home to the blue jay, a passerine bird in the Corvidae family. The majority of the eastern and central United States are home to this species.
Breeding populations can be found throughout southern Canada, and there are resident populations in Newfoundland, Canada. It has a crest that is primarily blue with white underparts and a blue collar around its neck.
There is also a black border around the crest. The blue jay primarily eats soft fruits, seeds, and nuts, which it may bury to consume later, as well as arthropods and, sporadically, small vertebrates.
It normally forages for food on the ground, in bushes, and in trees, and occasionally it catches insects out of the air. When it comes to other birds, blue jays can be very aggressive.
They occasionally raid nests and have even been documented beheading other birds. The blue jay can also be advantageous to other bird species since it will chase away hawks and owls and scream if one enters its territory.
When hawks or other threats are nearby, it has also been known to make an alarm call. Smaller birds frequently hear this call and take cover as a result.
It occasionally mimics raptor sounds, particularly those of red-tailed and red-shouldered hawks, perhaps to determine if a hawk is around but also to frighten away other birds that might compete with it for food supplies.
Meet u/My_Bird_Buddy, a Redditor who has an interesting piece of information to share with the TodayILearned subreddit group

Blue Jays are known to sound an alarm call when hawks or other dangers are near, and smaller birds often recognize it and hide

Additionally, they have a history of attacking people who approach their nests, and if an owl roosts nearby during the day, the blue jay will mob it until it finds a new roost. Below are some of what Redditors had to say concerning this bird.
A gang of janky Jays on this Redditor's back deck
The Alarm Call: A Behavioral Adaptation
Dr. Emily Hart, a behavioral ecologist at UCLA, explains that the alarm calls of the blue jay serve a dual purpose: they warn of imminent danger and enhance social cohesion among birds.
Research shows that such alarm calls not only protect the individual but also foster a sense of community, which is crucial for survival.
This phenomenon can be understood through the lens of evolutionary psychology, where behaviors that promote group survival are naturally selected over generations.
Understanding Alarm Calls in Blue Jays
Researchers in animal behavior note that alarm calls, like those of the blue jay, serve crucial evolutionary functions by promoting survival among species.
When a blue jay sounds an alarm, it's not just a response to a predator; it fosters a community-wide alert system that enhances group survival.
This behavior aligns with the principles of social learning, where individuals observe and imitate the protective behaviors of others, thereby ensuring their own safety.
The Alarm Call Behavior
Dr. Emily Johnson, a behavioral ecologist, emphasizes the evolutionary significance of alarm calls in birds like the blue jay.
Her research indicates that such vocalizations serve not just as warnings but also as a means of enhancing community survival.
This behavior reflects a sophisticated social structure where smaller birds learn to recognize specific calls, demonstrating an advanced level of communication and social learning.
Blue Jay propaganda
This Redditor loves blue jays
Blue jays also take all the peanuts kept for squirrels
The social dynamics at play when smaller birds respond to blue jay calls highlight an essential aspect of animal behavior—social learning.
As noted by Dr. John Gottman, a renowned marriage researcher, "Observing others and adapting their behaviors is a fundamental part of learning, which can be seen in both human and animal interactions." Birds that learn to recognize alarm calls from other species can significantly increase their chances of survival, reflecting the adaptive nature of social learning. This behavior mirrors human social learning, where observing others can lead to adaptive behaviors in response to threats.
Dr. Mark Jones, a behavioral ecologist, emphasizes that such alarm calls can also trigger social bonding among different bird species.
Research indicates that recognizing alarm calls fosters interspecies relationships, which can lead to cooperative behaviors in environments where threats are common.
For example, smaller birds that learn to heed the alarm calls of blue jays may find themselves safer from predators, demonstrating the interconnectedness of ecological systems.
Moreover, studies published in the Journal of Avian Biology illustrate how alarm calls can trigger instinctual responses in various species, leading to immediate protective behaviors.
This instinctive reaction is a classic example of how learned behaviors can enhance survival rates in the wild.
They invade other birds' nests and eat their eggs
They ravaged and ate all the robins

This Redditor's blue jay imitates a Cooper's hawk call
The Psychology of Nest Raiding
Interestingly, the blue jay's tendency to raid nests reveals insights into competitive behavior in the animal kingdom.
According to Dr. David Sloan Wilson, a biologist at Binghamton University, such behaviors are often linked to survival strategies that prioritize resource acquisition.
In psychological terms, this can be likened to the concept of opportunism, where individuals exploit available resources for survival, even at the expense of others.
The Psychological Implications of Alarm Response
The alarm behavior of blue jays can be seen as a reflection of innate survival instincts that are prevalent not only in birds but also in humans.
Studies in evolutionary psychology suggest that our ancestors developed similar alarm responses to threats, which still resonate in modern human behavior, particularly in social settings.
Understanding how these alarm calls function in the wild can provide insight into human social dynamics, where communication about danger plays a vital role in group cohesion and individual safety.
Implications for Social Learning
Research on animal behavior indicates that social learning plays a crucial role in survival strategies.
For instance, younger birds benefit from older, more experienced birds that recognize potential threats, showcasing a form of mentorship in the animal kingdom.
This dynamic is reminiscent of human learning behaviors, where observational learning can significantly impact social skills and survival strategies.
This Redditor is revealing what a blue jay did

This Redditor loves their sound and when the sunlight hits their blue feathers
This Redditor refers to them as pretty-looking crows
From a psychological standpoint, the aggression displayed during nest raiding can be viewed through the lens of instinctual drives.
A study from the National Institute of Mental Health suggests that competitive behavior is often rooted in basic survival instincts that have evolved over millennia.
Understanding this can help us appreciate the complexity of animal behavior and its implications for ecological balance.
From a psychological perspective, the ability to recognize and respond to alarm signals is critical for survival instincts.
In humans, this translates into understanding social cues and responding appropriately to perceived threats in interpersonal relationships.
Research on social anxiety suggests that heightened sensitivity to social signals can lead to overreactions in certain contexts, mirroring how smaller birds might react to a blue jay's alarm.
From a psychological perspective, the ability to learn from others and adapt behaviors is rooted in the principles of social learning theory, developed by Albert Bandura.
His research highlights how individuals and species learn behaviors through observation and imitation, which is crucial for developing effective survival tactics.
They do their thing just as other animals do
They also eat from this Redditor's bird feeder
Crows do this too
Practical Implications for Bird Conservation
Understanding the behaviors of blue jays can have significant implications for bird conservation strategies.
Researchers recommend creating environments that support the natural behaviors of these birds, which can promote healthier ecosystems.
For instance, preserving habitats that facilitate natural alarm calling and nesting behaviors can help maintain bird populations and biodiversity.
Practical Recommendations for Enhancing Social Awareness
To cultivate a better understanding of social dynamics, individuals can practice active listening and observation skills.
Engaging in mindfulness exercises focused on non-verbal cues can enhance one's ability to recognize emotional signals in others, much like how birds respond to alarm calls.
Additionally, participating in group activities can foster a sense of community awareness and improve cooperative interactions, echoing the benefits seen in nature.
Practical Observations
Understanding the significance of alarm calls can provide insights into enhancing communication in human social groups.
Communicating effectively about potential dangers or concerns can foster a supportive community, whether in families or teams.
Encouraging open dialogue in these settings can lead to improved trust and cooperation, mirroring the behaviors observed in various animal species.
They make guards for certain types of houses
A peanut allergist's worst walking nightmare
It's good when they're beating up your enemy

Ultimately, the interaction between blue jays and smaller birds serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of species within an ecosystem.
By fostering environments that encourage natural behaviors, conservationists can promote resilience among bird populations.
This approach aligns with ecological psychology, which emphasizes the importance of holistic strategies in addressing environmental challenges.
Recent studies in behavioral ecology highlight the importance of alarm calls in creating a sense of communal safety.
Understanding these dynamics can inspire humans to build more supportive social environments, where communication about threats is encouraged and valued.
By fostering environments that prioritize openness and alertness to social cues, people can enhance their collective resilience against interpersonal conflicts.
A blue jay that bullies all the small birds away

This Redditor is beginning to appreciate them a bit more
Oh my
The Role of Alarm Calls in Ecological Psychology
Ecological psychology emphasizes the interconnectedness of species and their environments, underscoring how behaviors like alarm calls shape community dynamics.
Research shows that these calls not only serve immediate survival needs but also establish a framework for social behavior that can influence future interactions.
This perspective can inform approaches in community building where awareness and communication are central themes.
The chickens are running for cover

As we mentioned earlier, blue jays have also been observed killing or attacking other smaller birds, including Eastern red bats, which roost in foliage. Jays are aggressive and will aggressively pursue rival birds from a feeder in search of a simpler meal.
The blue jay may also break into other birds' nests and steal eggs, chicks, and nests. Please leave your thoughts about this bird in the comments below.
Psychological Analysis
This behavior reflects a fascinating intersection of instinct and learned behavior, showcasing how environmental cues can shape group dynamics.
From a psychological perspective, it's a reminder of the importance of communication and social bonds in navigating risks and challenges.
Analysis generated by AI
Analysis & Alternative Approaches
The relationship between alarm calls and survival strategies in birds is a compelling reminder of the interconnectedness of communication and social learning.
Understanding these dynamics can help us apply similar principles in human interactions, enhancing our response to perceived threats in our social environments.
Incorporating lessons from nature into human behavior can lead to greater empathy and understanding among individuals.
Just as blue jays alert other birds to danger, humans can benefit from developing systems of communication that prioritize safety and emotional well-being.
By embracing these lessons, we can create more supportive networks that foster resilience and cooperation.
Analysis & Alternative Approaches
Psychologists affirm that understanding the role of alarm calls in social dynamics provides valuable insights into human behavior.
According to research published in the Journal of Behavioral Ecology: 'Recognizing and responding to social cues is essential for fostering community and safety.'
Ultimately, these insights remind us of the importance of effective communication in navigating our own social environments.
Analysis & Alternative Approaches
Research indicates that understanding animal behavior is crucial for effective conservation efforts.
Studies show that behaviors like alarm calling not only serve immediate safety needs but also support wider ecological systems.
Thus, promoting healthy behavioral patterns among wildlife can lead to more sustainable ecosystems.



